Migration
One of the first questions customers ask is how to integrated ACI with
existing brownfield classical ethernet networks. ACI is different in how
it handles learning and forwarding compared to traditional classic ethernet
switches that each treat the learning individually instead of as a whole.
Due to this specific configurations are required to achieve the goal of
connecting the two separate domains. There are two unique characteristics
that have to be configured in a bridge domain so that it will work properly.
- ARP Flooding: This parameters forces the ACI fabric to flood to
all ports in the same Layer2 domain any ARP requests that are received. In this
way any broadcast ARP requests that arrive from an external Layer 2 are forwarded
to all endpoints in the same layer 2 domain or to the exterior from inside the
ACI fabric
- Unknown unicast forwarding: This parameter also changes the behavior of the
ACI fabric to flood any unknown unicast entries to the ports of the same
layer 2 domain.
With these two parameter configuration changes completed the bridge domain
will behave the same way that a classical ethernet network behaves and makes
it possible to join a fabric layer 2 domain with a external layer 2 domain
for migration purposes. If you look at the following diagram you will see
this concept.
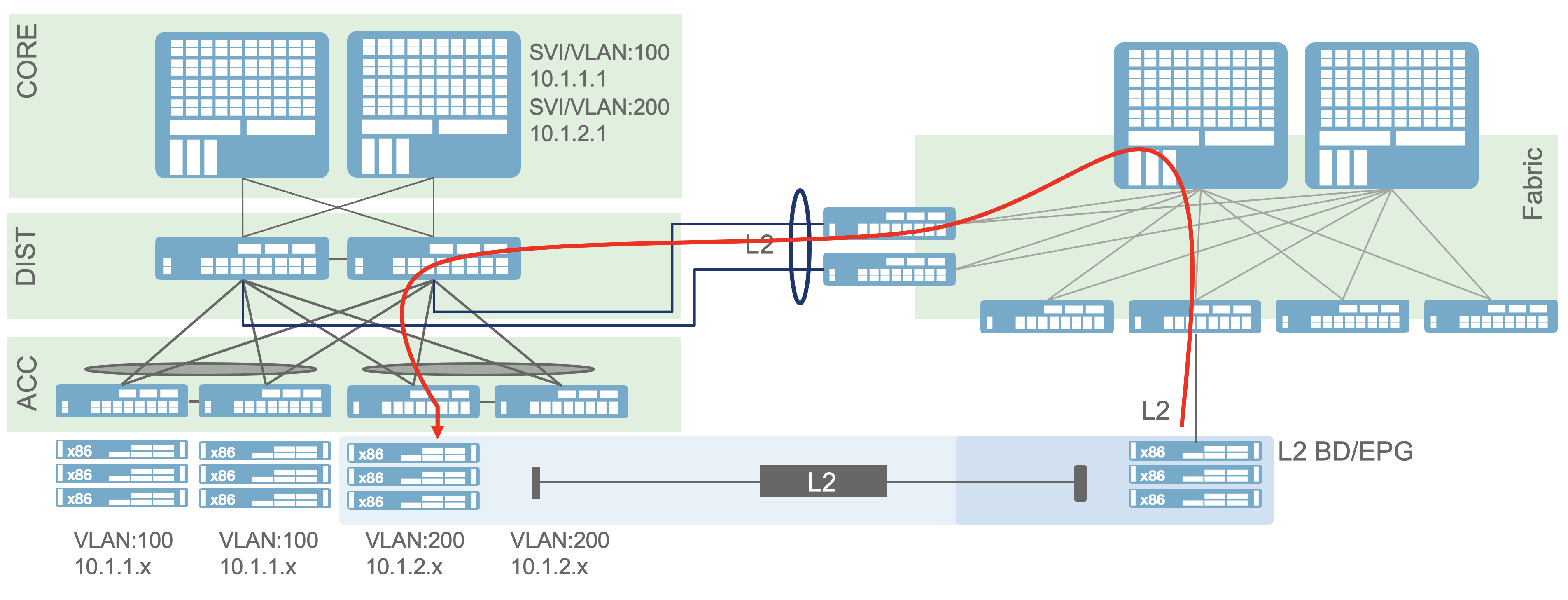
These servers in VLAN 200 inside the fabric can talk to the other servers
in the Layer2 domain outside. With these parameter definitions the
ACI fabric now modifies the fabric behavior so that these devices can
function properly.
You may be asking how does Layer 3 default gateway work. In the same
fashion the layer 3 default gateway lives outside the ACI fabric and
the devices in the fabric will use that as the default gateway.
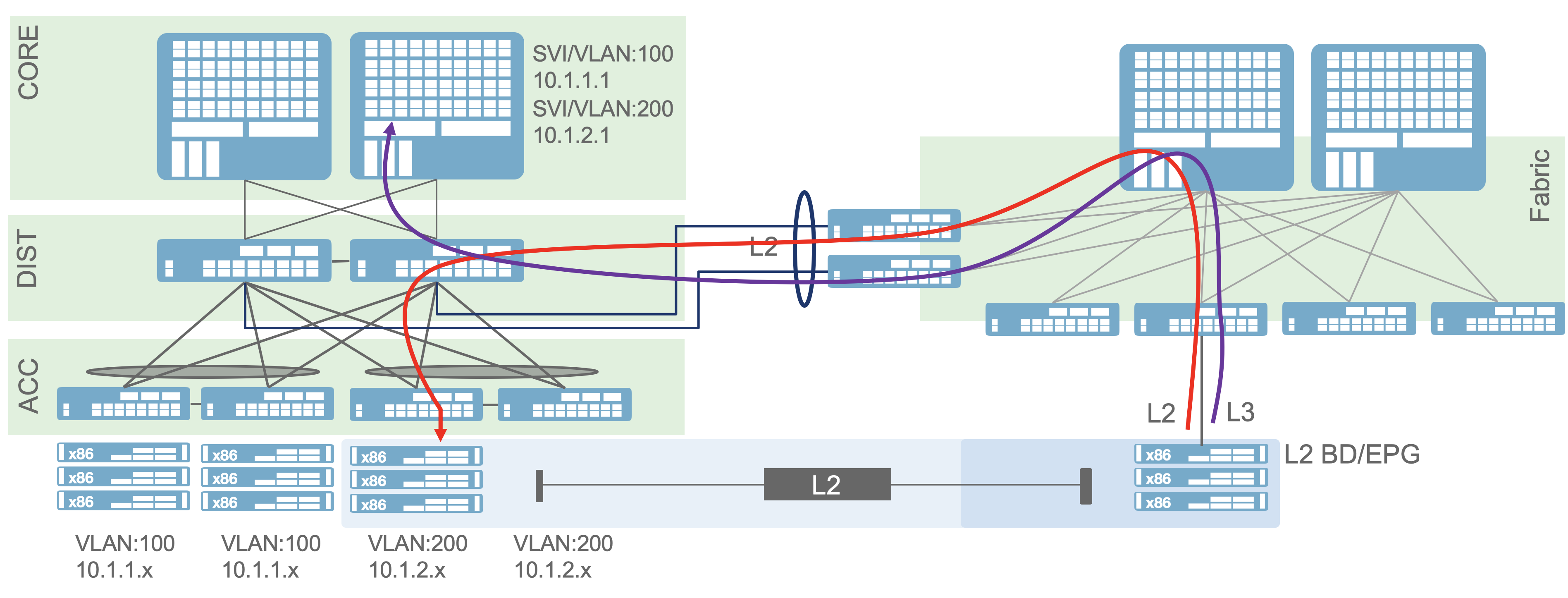
With this setup it becomes simple to migrate workloads into the ACI
fabric. When all the endpoints of the layer2 domain have been migrated
into the ACI fabric, the bridge domain can be reconfigured on the fly
to include the default gateway and integrate with a fabric layer 3
external to continue operating 100% inside the fabric.
For the lab you will be configuring specific parameters of this
Layer 2 bridge domain to observe the functionality. The following
tables expands on the concepts we have shown.
|
Property
|
Description
|
|
Forwarding
|
Custom Custom Reveals the Unicast and ARP selections for custom configuration.
|
|
Unicast Routing
|
Enables/Disbles Unicast Routing on the BD
|
|
L2 Unknown Unicast
|
Flood Enables the BD to flood L2 Unknown traffic.
|
|
ARP Flooding
|
Allows the BD to Flood ARP within the BD
|
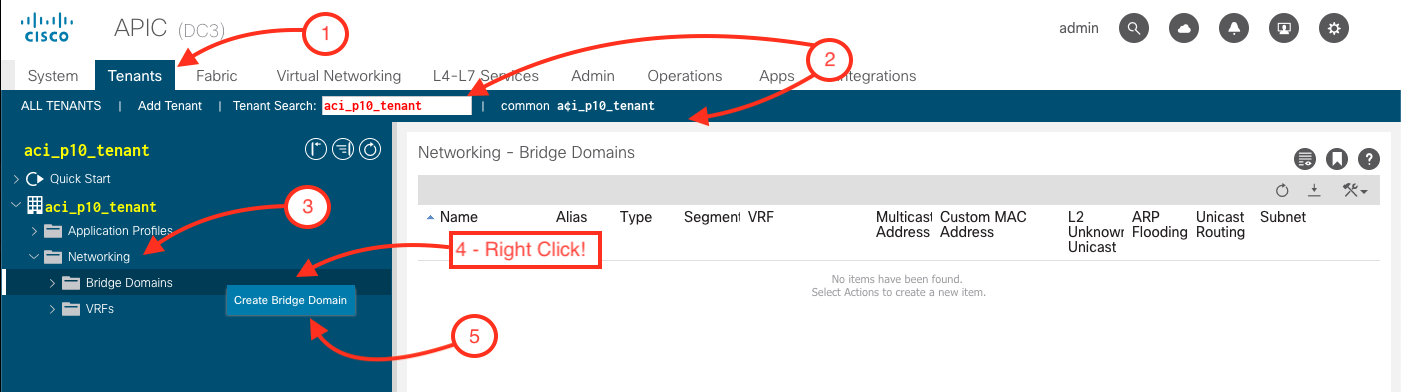
Step 1 - Navigate to Bridge Domains in the Tenants Tab under Networking
Navigate to Networking to create a Bridge Domain by clicking:
- Click on Tenant
- Expand Networking
- Right-click on Bridge Domains
- Click Create Bridge Domains
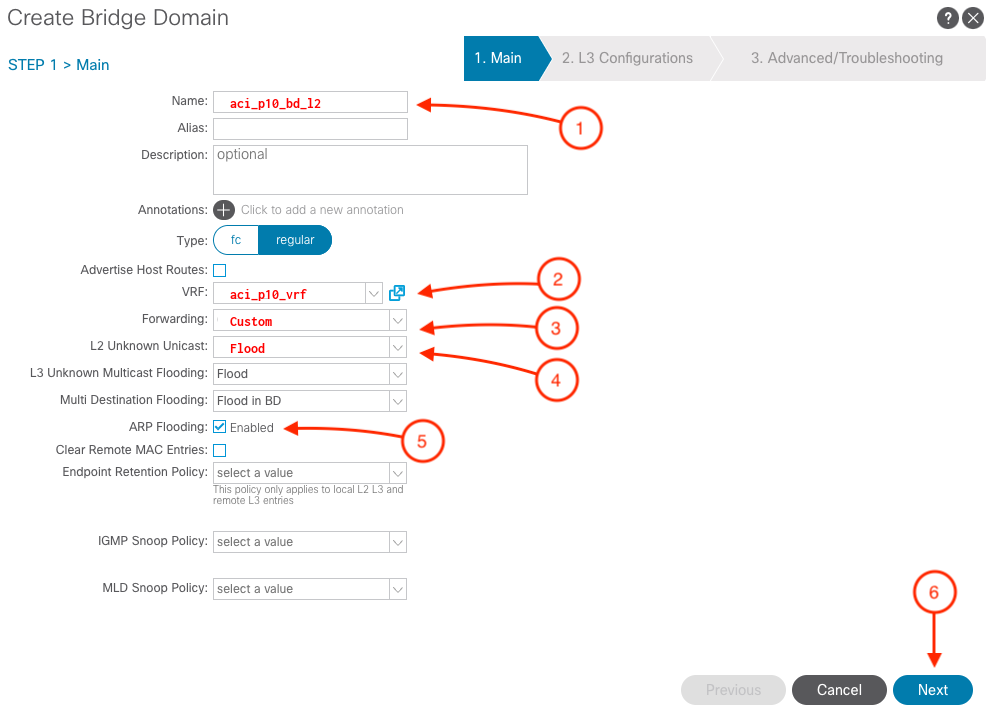
Step 2 - Create Layer 2 Bridge Domain (BD)
-
Name the
aci_p10_bd_l2
- Select the VRF aci_p10_vrf
- Forwarding = Custom
- L2 Unknown Unicast = Flood
- ARP Flooding = Checked
- Click Next
- Uncheck Unicast Routing
- Click Next
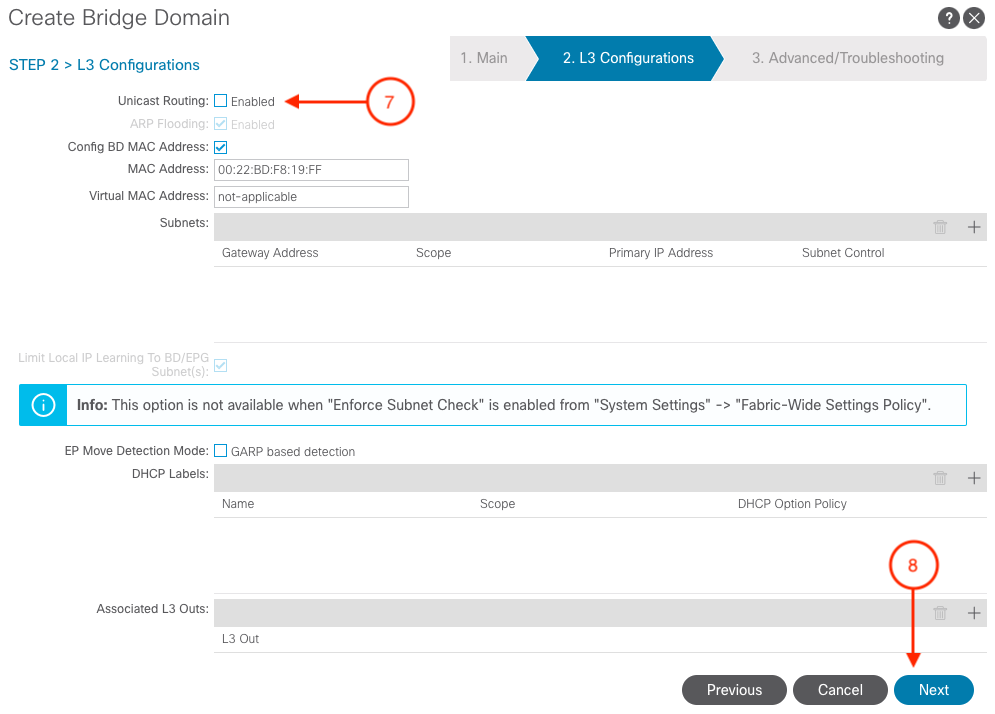
- Click Finish
Please verify your work before proceeding.
ACI Object
This is the response from the fabric as to what is configured.





