- Introduction
- ACI Basics
- Access Policies
- ACI VMM Integration
- Tenants
- Day 2 Operations
- Endpoint Security Group
- ACI Segmentation
- Nexus Dashboard
- Orchestrator
- Insights
- Conclusion
- References
What is ACI?
Cisco ACI is a tighly coupled policy-driven solution that integrates hardware and software in which the switches are based of the
Nexus 9000 product line and an APIC controller which runs in the Cisco UCS platform. The software that runs in the APIC controller is an image which
contains the ACI policy model and becomes the Single Paned Glass to manage and operate the Cisco ACI fabric. The software that runs in the switches is a
single
binary image for both fix and modular chassis providing an easy way to manage software within the switches in the fabric.
Cisco ACI has become the standard SDN solution for many customers across different industries. One of the main reasons for this is because of its
flexibility to manage and have visibility into different environments including Virtual, Physical and Container. ACI's architecture is based on a
spine-leaf (CLOS) model where ECMP is leveraged between the spine switches and leaf switches, thus providing IP redundancy across the entire fabric. W
ithin the fabric, ACI uses standard VXLAN in order to forward data between any device within the fabric.
Cisco ACI can also support L4-L7 devices within the fabric in order to provide the automation requirement for advanced security features, load balancing
capabilities, monitoring, etc. Cisco ACI supports
different vendors including Cisco, F5, AVI, etc. Please check the following link to obtain the latest support matrix:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/data-center-virtualization/application-centric-infrastructure/index.html
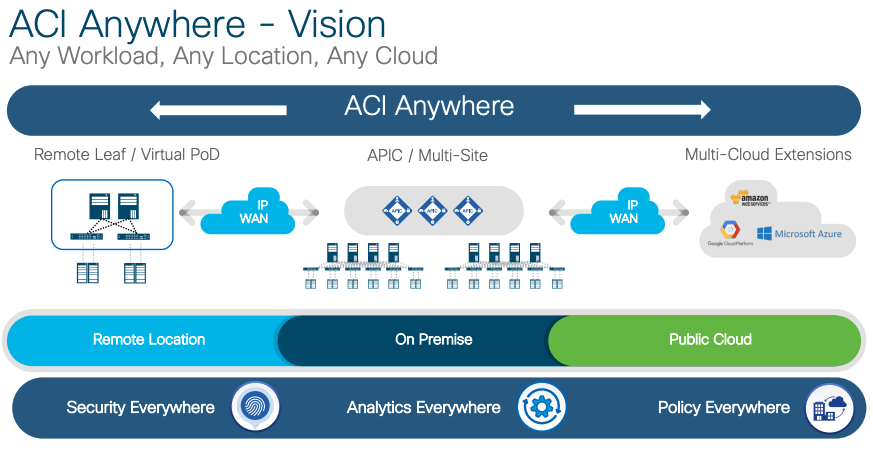
Because of their success with ACI, customers started asking how they could extend the ACI policy outside of their single Data Center. Therefore,
from these requests, a vision to extend the ACI policy outside the initial Data Center has been introduced as the "ACI Anywhere" concept.
Customers can now connect multiple Data Centers with the Cisco MultiSite Orchestrator (MSO), also referred to as the Cisco MultiSite Controller
(MSC), where the MSO becomes your geographical data center Single Pane of Glass. It is used to handle the visibility into various data center
sites and the rendering of the policies across the respective data center sites. Another feature that customers can leverage is the "Remote Leaf"
concept, where customers can extend ACI to Satellite Data Centers. Also, customers can extend the same ACI Policy to Bare Metal clouds and Remote
Data Centers with "Cisco ACI vPOD". Lastly, Cisco ACI Policy framework can be extended to any Public Cloud such as AWS, Google Cloud and Azure.
Below is the ACI Anywhere vision for your reference.
Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller
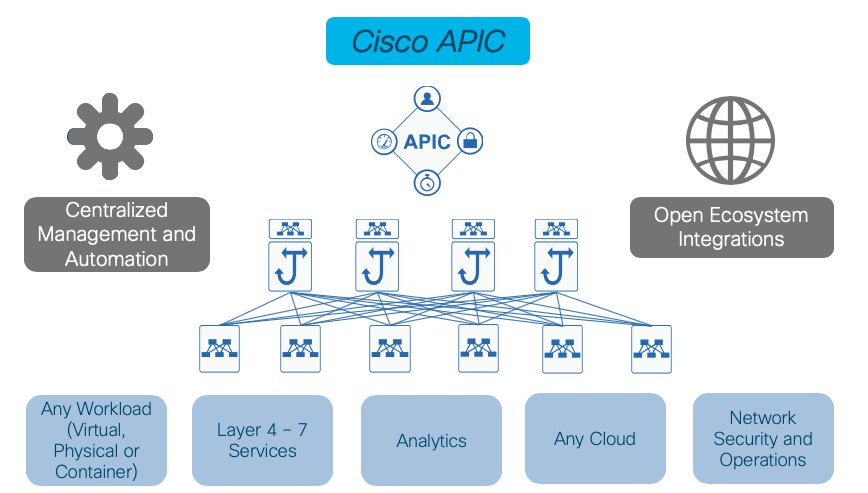
Cisco APIC serves as the single point of automation and fabric element manager in both physical, virtual and container environments.
As a result, operators can build fully automated and scalable multitenant environments.
Cisco APIC is a unified point for policy-based configuration expressed through group-based policy with the idea to make it simple for the operators.
Cisco APIC attributes and features include the following:
- The ability to build and enforce application centric network policies
- An open framework through northbound and southbound APIs
- Integration of third-party Layer 4 through 7 services, virtualization, and management
- Intelligent telemetry and visibility for applications and tenants
- The ability to provide security for multitenant environments at scale
- A common policy platform for physical, virtual, container, and cloud networking
Cisco APIC communicates with the Cisco ACI fabric to distribute policies to the points of attachment and provide several
critical administrative functions to the fabric. Cisco APIC is not directly involved in data-plane forwarding, so a complete
failure or disconnection of all Cisco APIC elements in a cluster will not result in any loss of forwarding capabilities,
increasing overall system reliability.
In general, policies are distributed to nodes as needed upon endpoint attachment or by an administrative static binding,
allowing greater scalability across the entire fabric.
Cisco APIC also provides full native support for multitenancy so that multiple interested groups (internal or external to
the organization) can share the Cisco ACI fabric securely, yet still be allowed access to shared resources if required. Cisco
APIC also has full, detailed support for role-based access control (RBAC) down to each managed object in the system, so that
privileges (read, write, or both) can be granted per role across the entire fabric.
Cisco APIC also has completely open APIs so that users can use Representational State Transfer (REST)-based calls
(through XML or JavaScript Object Notation [JSON]) to provision, manage, monitor, or troubleshoot the system. Additionally,
Cisco APIC includes a CLI and a GUI as central points of management for the entire Cisco ACI fabric.
Cisco ACI Fabric
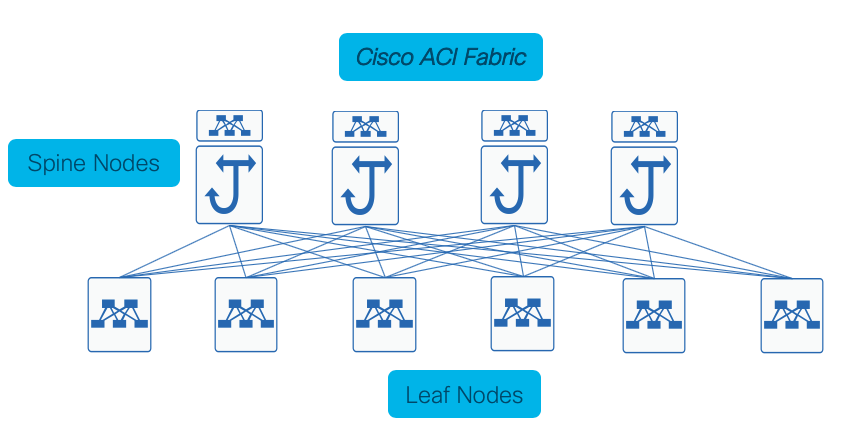
The Cisco ACI Fabric is built around a set of hardware to provide the most scalable, extensible, simple, flexible, and
efficient network in the industry. The Cisco ACI fabric is designed to address both today's and tomorrow's requirements:
- Scalable Fabric: The Cisco ACI Fabric is designed around the spine and leaf architecture in which every spine is connected to every leaf.
- Extensible: The Cisco ACI Fabric is highly extensible where System Administrators can integrate virtual network via VMWare or Microsoft System
Center Virtual Machine Manager as well as Layer 4 through 7 services such as firewalls, load balancers, IDS, etc.
- Simple: The Cisco ACI Fabric is built around in a very simple way leveraging Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) as the
single Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) and standard based Virtual Extensible (VXLAN) provides a simple overlay for tenant-facing traffic,
supporting full Layer 2 bridging and Layer 3 routing across the entire fabric
- Flexible: The Cisco ACI Fabric allows for users to attach any host across the entire fabric. The Fabric can provide normalization
for multiple types of encapsulation such as VLAN, VXLAN, and NVGRE. This feature allows physical, virtual and container-based hosts to
all co-exist on the same shared infrastructure.
- Efficient: Because of the inherit spine - leaf architecture every host is exactly two physical hops away from every other host in the
fabric. The Cisco ACI fabric can exceed other traditional spine-and-leaf fabrics in fabric bandwidth efficiency, because it
can take into account packet arrival time, end-to-end fabric congestion, and flowlet switching to make more intelligent
load-balancing decisions. More information about these innovations is documented in the SIGCOMM paper
“CONGA: Distributed Congestion-Aware Load Balancing for Datacenters”.
In the next section, you will examine how the APIC is initiated before examining the APIC and fabric connectivity.




